Selected Projects
Classifying arXiv Math Publications By Subject
The arXiv is a large free repository hosting papers across many STEM disciplines. This project is multi-label classification model which predicts the relevant subject tags of a math paper based only on its title. The details of model development are explained below.
Inference Pipeline
Preprocessing
- The title is retrieved from the input ID via a call to the arXiv API.
- The title string is cleaned–inline LaTeX is removed, all accented characters are converted to their ASCII equivalents, LaTeX environments not enclosed by $ signs are removed.
Huggingface Model
- The model consists of a pretrained
bert-base-uncasedtransformer and a single layer neural network ‘classification head’. - The input sentence (clean title) is encoded using this BERT model and its pooled output is run through the classification head.
- The model consists of a pretrained
Postprocessing
- The classification head outputs a vector whose \(j^{th}\) component is the probability that the \(j^{th}\) label is relevant.
- A minimum probability threshold required to predict a label is passed in and the vector of subject tag probabilities is converted into a list of english named subject tags.
Model Training
The huggingface model is an example of a “fine-tuned” model. The transformer model responsible for generating the vector representation of the input text is pretrained, and these weights are not modified. However, the classification head is trained on a dataset consisting of about 40,000 (title,label) pairs. This dataset was extracted from a random sample of 10% of all of the math articles contained in the full arXiv kaggle dataset
A Nearest-Neighbor Based Recommender System for Math Articles
This project returns the 5 most similar math articles to a provided article.
Model Design
We start with a chosen library of articles from which we make recommendations. Using their title and abstract, every article is embedded in a vector space in such a way that papers pointing ‘in the same direction’ are similar in content. To make recommendations, the input article is embedded in the same way and its 5 nearest neighbors in the library are calculated.
We use the allenai-specter sentence transformer as our embedding model. This model has been pre-trained on a large corpus of scientific articles specifically for the task of detecting semantic similarity.
Unsupervised Topic Modeling
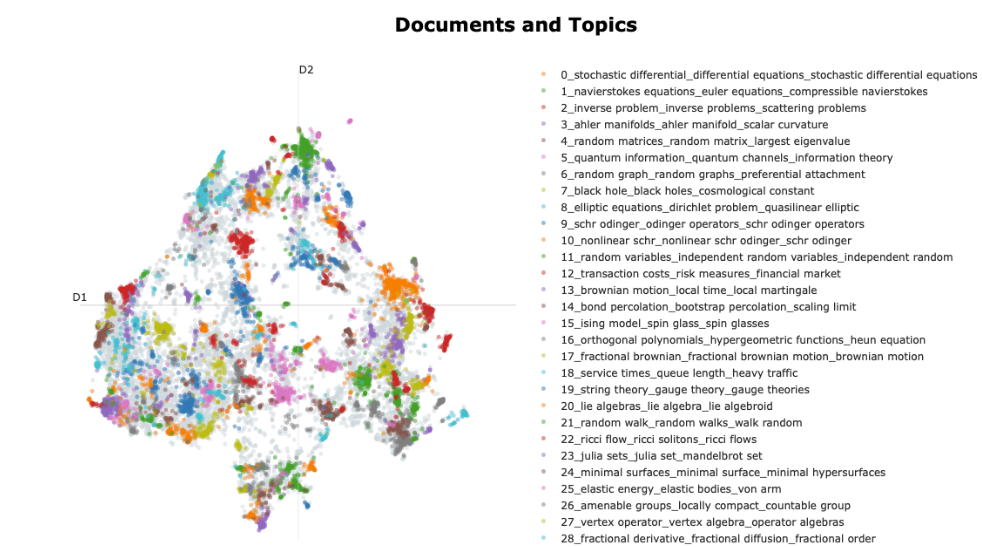
- Additionally, we performed unsupervised topic modeling on our recommendation library using BERTopic. BERTopic works by applying the HDBSCAN. clustering algorithm on the embedded articles. A variant of tf-idf is then run on each cluster to extract the common topics present. Here is a picture of the embedding space after applying the UMAP dimension reduction. Keywords for the strongest topic clusters are shown on the right.
Stanford CS229 “Intro to Machine Learning” Personal Notes and Problem Set Solutions
The following is a collection of notes and exercises written while following the Stanford CS 229 “Intro to Machine Learning” course. Full repository of course materials can be found here. All lectures are available on YouTube.
Problem Set 0
Problem Set 1
Problem Set 2
Problem Set 3
